How to Choose the Right Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor for Your Engine
Brian Craig
May 10, 2023
Exhaust gas temperature (EGT) sensors are crucial components in modern engines, particularly those with forced induction systems. Exhaust gas temperature sensors are provide real-time temperature readings of the exhaust gases that are used by the engine control unit to regulate fuel injection and ignition timing.
By monitoring exhaust gas temperature, the engine control unit (ECU) can optimize engine performance, reduce emissions, and prevent damage to the engine caused by overheating. This blog post will provide a comprehensive guide on how to choose the right exhaust gas temperature sensor for your engine. It will cover the different types of EGT sensors available, how they work, factors to consider when choosing one, key features to look for, installation and maintenance tips, and common problems that may arise.
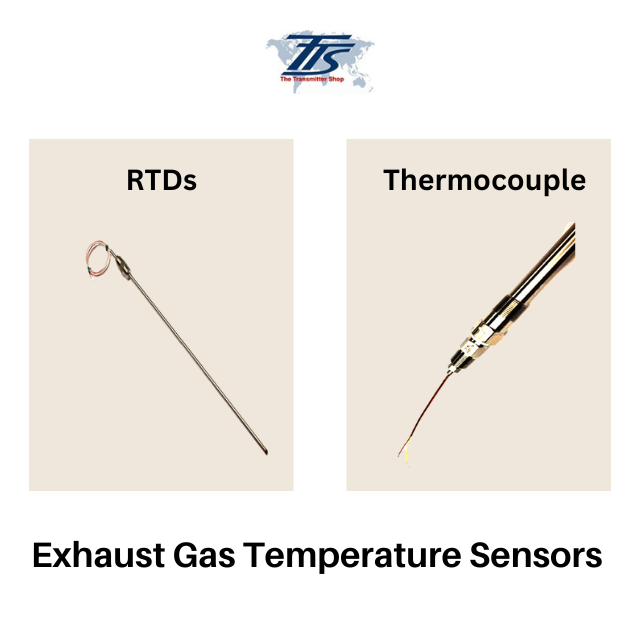
What is an Exhaust Gas Temperature (EGT) Sensor?
An Exhaust Gas Temperature (EGT) sensor is an electronic device that measures the temperature of the exhaust gases in a combustion engine. The sensor is typically installed in the exhaust system and is used to monitor the temperature of the exhaust gases in real-time. These sensors helps to optimize the fuel-air mixture and ensure the efficient operation of the engine. It is also used to monitor the performance of emission control systems and to prevent damage to the engine caused by excessive heat. The sensor can be of various types, including thermocouples and resistance temperature detectors.
How an Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor Works?
Exhaust gas temperature sensor works with temperature-sensing elements such as thermocouples, resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), infrared sensors and gas temperature probes that are installed in the exhaust system. The sensor measures the temperature of the exhaust gases and converts it into an electrical signal that sent to the engine control unit.
The engine control unit uses the data to optimize the engine's fuel-air mixture, adjust the engine's performance, and prevent damage to the engine caused by excessive heat. The type of sensing element used depends on the specific application, and each type has its benefits and limitations.
Types of Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensors
There are different types of exhaust gas temperature sensors available in the market with its unique advantages and limitations. Here we will discuss the different types of exhaust gas temperature sensors and their characteristics.
- Thermocouple: Thermocouple is a type of exhaust gas temperature sensor that works based on the principle of Seebeck effect. It consists of two different types of metal wires joined at one end, forming a junction. When the junction is exposed to a temperature difference a voltage is generated, which can be measured to determine the temperature. Thermocouples are widely used in exhaust gas temperature measurements due to their wide temperature range, high accuracy, and fast response time.
- Resistance Temperature Detector (RTD): Resistance Temperature Detector (RTD) is another type of exhaust gas temperature sensor that works based on the principle of the resistance change of metal wires with temperature. An RTD is typically made of a metal wire, such as platinum or nickel, whose resistance increases with temperature. The change in resistance is then measured to determine the temperature. RTDs are known for their high accuracy, stability, and repeatability, making them suitable for precise temperature measurements in exhaust gas applications. However, they are generally slower in response time compared to thermocouples.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor
- Type of engine: The type of engine you have will determine the type of EGT sensor you need. For example, diesel engines typically require thermocouple sensors due to their high exhaust gas temperatures, while gasoline engines may use either thermocouple or RTD sensors.
- Type of fuel used: The type of fuel you use can also affect the choice of EGT sensor. Different fuels produce different exhaust gas temperatures, and sensors need to be calibrated to provide accurate readings for each type of fuel.
- Operating conditions: The operating conditions of your engine, such as its load and RPM range, can also affect the choice of EGT sensor. For high-performance engines that operate at high RPMs, fast-response thermocouple sensors may be needed to provide accurate temperature readings.
- Budget: The cost of EGT sensors can vary widely depending on their features and quality. It's important to choose a sensor that provides the necessary accuracy and durability for your engine, while staying within your budget.
Features To Look For In an Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor
- Durability: EGT sensors are exposed to high temperatures and harsh environments, so it's important to choose one that is built to last. Look for sensors made from high-quality materials and with a proven track record of reliability.
- Accuracy: Accuracy is crucial when it comes to EGT sensors, as even small variations in temperature readings can have a big impact on engine performance. Look for sensors that provide precise and consistent temperature readings.
- Response time: The response time of an EGT sensor is the time it takes for the sensor to detect and report a change in temperature. Fast-response sensors are essential for high-performance engines that require precise temperature control.
- Compatibility: Make sure that the EGT sensor you choose is compatible with your engine and ECU. Some sensors may require.
Exhaust Gas Temperature sensors play a crucial role in optimizing engine performance, reducing emissions, and preventing damage to the engine caused by overheating. By choosing the right EGT sensor and properly installing and maintaining it, you can ensure the efficient and safe operation of your engine. The Transmitter Shop (TTS) is a distributor of superior quality remanufactured thermocouple, RTDs, Thermometer, Transmitters and Thermowells originally sourced from reputed brands such as Rosemount, Foxboro, Thermo-Probes and so on. The company specializes in remanufacturing, reconditioning, and calibration of devices.
Related Posts
- What is RTD Sensor and How Does it Work?
- What is a Thermocouple and How Does It Work?
- A Beginner’s Guide for Installation of Thermowell
- Why Platinum is a Preferred Choice in RTD Sensors?
- How to Choose the Right Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor for Your Engine
- Role of Sensors in the Food Processing Plant
- Steam Boiler Drum Level Measurement A Comparison of Control System Technologies
- Furnace Flame Sensor Faults Everything You Need to Know for Safe Operation
- Comparison between Multi Valve Manifolds Block Valves and Bleed Valves
- Understanding Electrochemical Detection: Principles, Techniques and Environmental Application
- How Can Greenhouse Gas Emissions Be Reduced?
- Furnace Flame Sensor Faults Everything You Need to Know for Safe Operation
- Understanding Electrochemical Detection: Principles, Techniques and Environmental Application
- How Can Greenhouse Gas Emissions Be Reduced?
- Pneumatic Pressure Controllers: A Safe Choice for Hazardous Areas
- A Practical Guide to Vacuum Measurement and Operation
QUICK ENQUIRY







